
Reimagining medicine
We are developing potentially transformational therapies for diseases with high unmet needs.
Explore our lead programs
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a rare, genetic neuromuscular disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene on the X chromosome, which leads to progressive, irreversible loss of muscle function, including the heart and lungs.
DMD primarily affects boys and can rarely affect girls. Individuals with DMD typically develop muscle weakness in the early years of life and become wheelchair-bound in their early teens. As the disease progresses, individuals with DMD typically develop respiratory, orthopedic, and cardiac complications, with cardiomyopathy and breathing difficulties beginning by the age of 20. It is ultimately fatal.
~1/5,000
newborn boys around the world
~20K
new cases of DMD annually worldwide

Spencer, living with DMD

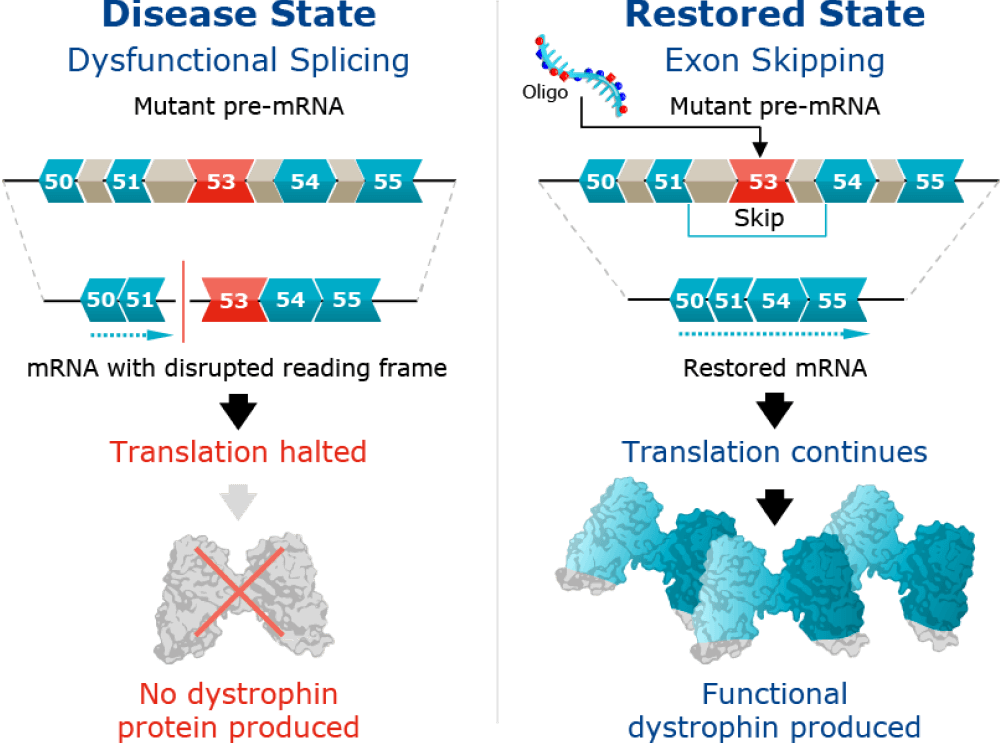
The cause of DMD
DMD is a genetic disease caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene that prevents the production of dystrophin protein, a critical component of healthy muscle function.
In skeletal and cardiac muscles, the dystrophin protein is part of a protein complex called the dystrophin-associated protein complex that acts as an anchor, connecting each muscle cell’s structural framework with the lattice of proteins and other molecules outside the cell through the muscle cell membrane. The dystrophin-associated protein complex protects the muscle from injury during contraction and relaxation. Without dystrophin protein, muscle tissue is replaced by fat cells and muscles deteriorate over time.
Our Approach
Our clinical-stage DMD program, WVE-N531, is designed to skip exon 53 and restore the mRNA reading frame. This would enable restoration of functional, endogenous dystrophin protein.
Read the latest news on WVE-N531
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is an inherited genetic disorder that is commonly caused by a G-to-A point mutation in the SERPINA1 gene, termed the Z allele.
200,000
people in the United States and Europe have two copies of the Z allele, which is the most common form of severe disease.

Dan, living with AATD

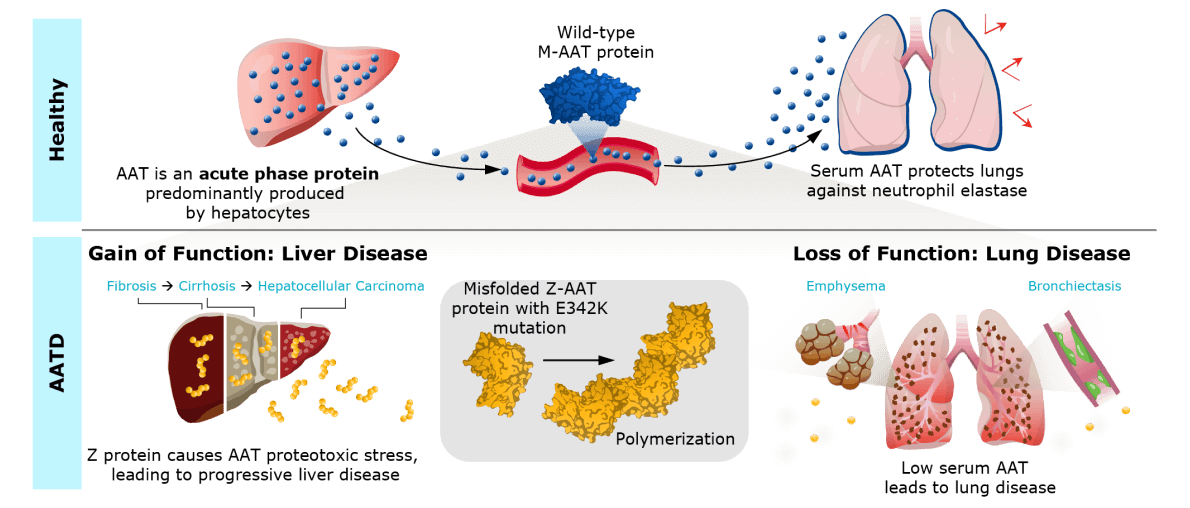
The cause of AATD
The Z mutation leads to misfolding and aggregation of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) protein in hepatocytes and a lack of functional AAT in the lungs, leaving them exposed to damage from proteases. People with AATD typically exhibit progressive lung damage, liver damage, or both, leading to frequent hospitalizations and potentially fatal lung disease and/or liver disease.
Our Approach
Our clinical-stage AATD program, WVE-006, is our first program to leverage our novel RNA editing capability and the industry’s first RNA editing compound to enter the clinic. It is designed to correct the single base in the mutant SERPINA1 mRNA by reverting the mutant A to an I, which cells read as G. This approach would reduce AAT protein aggregation in the liver, restore circulating, functional wild-type AAT to protect the lungs from proteases, and retain physiological regulation of the AAT protein. In this manner, WVE-006 may offer a single treatment approach for AATD-related liver disease, lung disease, or both.
Read the latest news on WVE-006
Huntington’s disease
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a hereditary neurodegenerative disease that impacts generations within each affected family.
Many describe the symptoms of HD as similar to having amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease simultaneously. Life expectancy after symptom onset is approximately 20 years.
~30K
people in the US are estimated to be gene-positive for HD and exhibiting symptoms.
~200K
people in the US are estimated to be at risk of developing the condition.

Brett and Kyle, living with HD


The cause of HD
HD is caused by a mutation in the huntingtin (HTT) gene. Specifically, an expanded section within the gene (CAG triplet repeat) results in production of an expanded huntingtin protein (mHTT). Accumulation of mHTT causes progressive loss of neurons in the brain and can lead to neuronal cell death, causing motor, cognitive, and psychiatric disability.
HD patients still possess some wild-type (healthy) HTT (wtHTT) protein, which is important for neuronal function and which may be neuroprotective in an adult brain. Studies suggest a multifaceted mechanism by which gain of mHTT protein and a concurrent loss of wtHTT protein may drive the pathophysiology of HD. Accordingly, therapeutic approaches for HD that aim to lower mHTT but also suppress wtHTT may have detrimental long-term consequences.
Our Approach
Our clinical-stage HD program, WVE-003, is an antisense oligonucleotide designed to selectively target an undisclosed SNP (SNP3) associated with the disease-causing mutant huntingtin (mHTT) mRNA transcript within the HTT gene. SNPs are naturally occurring variations within a given genetic sequence and in certain instances can be used to distinguish between two related copies of a gene where only one is associated with the expression of a disease-causing protein. Targeting mRNA with SNP3 allows us to lower expression of mHTT protein, while preserving the healthy wtHTT protein. This approach may also enable us to address the pre-manifest, or asymptomatic, HD population in the future.
Read the latest news on WVE-003
Obesity
Obesity impacts approximately 174 million people in the US and Europe. In the United States alone, obesity costs the US healthcare system nearly $173 billion a year.
The recent emergence of new medicines that can treat obesity, known as glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, has brought renewed focus to and appreciation for this health condition as a chronic illness with significant comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. However, high unmet needs remain. GLP-1 receptor agonists lead to weight loss at the expense of muscle mass, suppress the general reward system, and are associated with poor tolerability profiles and discontinuation rates as high as 70%. A therapeutic approach for obesity that improves metabolism, increases fat loss, maintains muscle mass, and does not affect the general reward system would be ideal.
174 million
adults in the US and Europe impacted by obesity.
$173 billion
cost impact on US healthcare system every year.
Our Approach
Wave is developing a new therapeutic option to treat obesity and other metabolic disorders that uses RNA interference (RNAi) to silence the INHBE gene. There is strong genetic evidence supporting this target, as carriers of heterozygous loss of function variants of the INHBE gene exhibit several beneficial traits, including reduced waist-to-hip circumference, reduced risk for type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease, and lower serum triglycerides.
Silencing INHBE by 50% or more with siRNA (small interfering RNA) is expected to restore a healthy sustainable metabolic profile.
Read the latest news on our INHBE program
